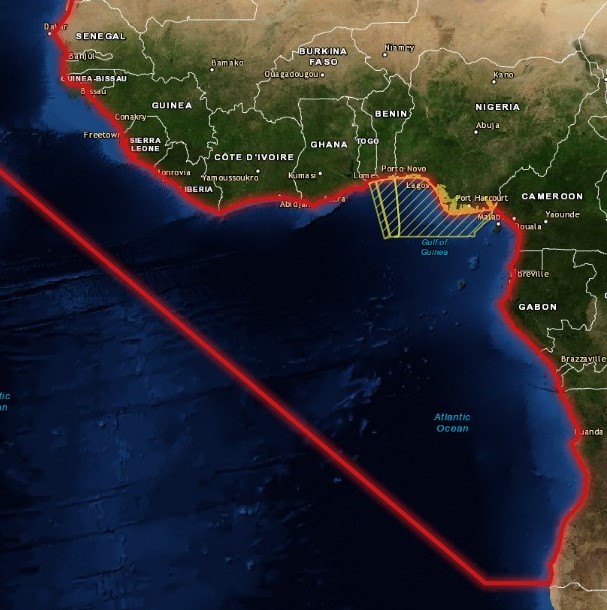
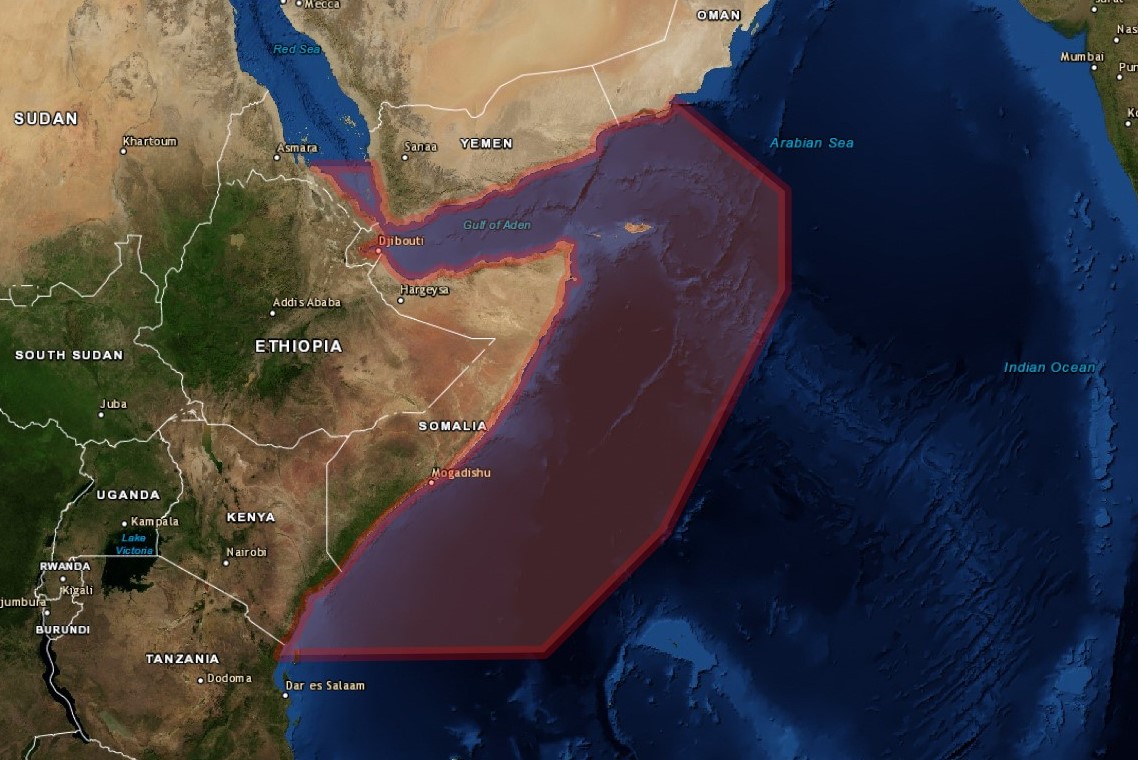
Differences between piracy in East and West Africa
There is a significant difference between the modus operandi of Nigerian pirates and counter piracy operations in the Gulf of Guinea and the Horn of Africa.
Most attacks take place in the Gulf of Aden which is classed as international waters, allowing the international community to protect ships. At the peak of maritime crime in the Horn of Africa 30 countries provided ships for this purpose.
However, in the Gulf of Guinea, the majority of attacks occur near the coast, these waters are territorial and the responsibility of the coastline’s State. The nations themselves have to intervene.
International Attention... or lack of
These closer to shore incidents in West Africa tend to be high volume, low level maritime crime incidents such as robberies. These incidents were few and far between in the Indian Ocean with the primary focus offshore incidents, such as kidnappings and hijackings by Somali pirates. Another key difference is that West African criminals and Nigerian pirates have the capability to board larger vessels in deep offshore waters.
The Indian Ocean as a link to the Red Sea, and therefore the Mediterranean, makes the Horn of Africa one of the world's busiest and therefore an extremely important shipping route. When Somali piracy flared up an immense level of international power was on hand because capable coalition resources and western states with vested regional interests had already placed deployable assets in the area to safeguard its strategic importance as a high volume sea trade route and protect large flows of goods transported from Europe to Asia.
The EU swiftly launched Operation Atlanta in 2008, a European mission to secure the region's water for shipping. In West Africa, the international communities response has, to date, been minimal.
International Missions

International missions are extremely important to combat piracy effectively. They enable the exchange of information and knowledge between countries that have resources and those that are struggling with addressing maritime crime. Within territorial waters it is impossible for any international navy to enter; however, they can help to train coastguards in how to react to an attack or arrest pirates. They can also educate the local community to help them understand the negative effects of facilitating maritime crime from land.

